If you have been wanting to start a career in the healthcare industry, you might be confused about which job profile to choose from.
Working in the field of healthcare comes with its own perks. If you want to work directly with patients, you can consider becoming a phlebotomist or a medical assistant.
Both these careers are in demand and highly rewarding. Now you might be confused about which one of these is the best suited for you.
Medical assistants and phlebotomists both play essential roles in providing patient care. Read on to learn more about the differences and similarities between these two careers that might help you choose the best-suited career.
Also see: 12 Reasons to Become a Medical Assistant
Medical Assistants vs. Phlebotomists: Overview
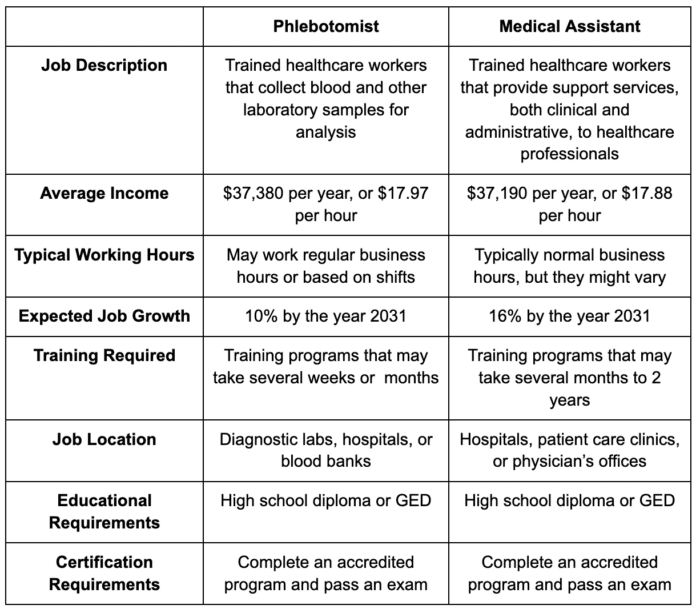
Medical assistants are trained healthcare workers who provide support services to physicians and other healthcare professionals. Medical assistant job duties include clinical and administrative tasks, ranging from assisting physicians with bedside procedures to scheduling appointments.
Medical assistants work near physicians in different healthcare settings, such as hospitals or outpatient care clinics.
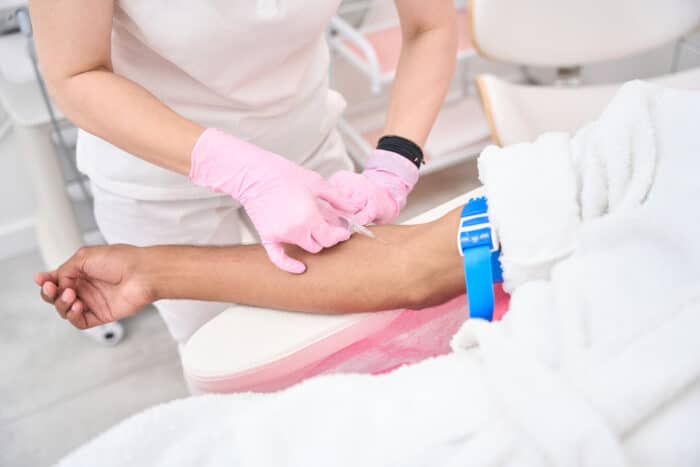
Phlebotomists are healthcare workers who specialize in drawing blood and collecting other samples for analysis.
These healthcare workers must have a foundational knowledge of the transportation, storage, and collection requirements of the various types of collected samples.
Both these careers are considered important for a healthcare system to function smoothly. Even though there are similarities, there are also many differences between a medical assistant and a phlebotomist.
Let us take a look at a brief overview of phlebotomist and medical assistant careers:
Medical Assistants: Overview
Medical assistants are considered to be the backbone of the healthcare industry. These healthcare workers perform both clinical and administrative tasks, which include:
- Scheduling appointments
- Assisting physicians with bedside procedures
- Recording patients’ vital signs
- Maintaining patients’ medical histories
- Handling the payments and billings
- Collecting and sampling specimens for laboratory testing
- Prepping patients and examination rooms before each patient visit
The minimum prerequisite for becoming a medical assistant is to complete your high school diploma or a GED.
After obtaining your high school diploma, you will need to complete your medical assistant training from an accredited institution.
Generally, there are three main methods of completing your medical assistant program, such as-
- Obtaining an associate’s degree from a technical university
- Getting a diploma from a community college
- Completing an online training program
See more on: Medical Assistant Degree vs Certificate
Completing your training by choosing an online training program is the most recommended option since it has many advantages over its alternatives.
Read more on: Is Medical Assistant Degree Required?
Here are a few reasons why you should choose an online training program instead-
- You can complete your training faster, in as little as six months.
- You can learn at your own pace and schedule and at the comfort of your own home.
- An online training course costs way less than its alternatives so that student loans do not burden you (See: Medical Assistant Programs Cost).
- Online training programs also prepare you for certification exams, which help you become a certified medical assistant and start your career with ease.
Also see: Medical Assistant Certificate Requirements
Even though most states do not necessarily need you to be licensed or certified, employers highly prefer certified candidates, and they also tend to earn 10% more than uncertified ones (Also see: Medical Assistant Scope of Practice by State).
See also: Are Medical Assistant Licenses Required?
Medical assistants are employed in diverse settings, such as doctor’s offices, clinics, and outpatient centers, with typical daytime business hours, though some may have weekend or evening shifts.
A medical assistant’s daily routine varies depending on their workplace and role, with responsibilities that can change rapidly throughout the day.
For instance, you may start by checking patients in and measuring vital signs in the morning and later assist a physician with procedures like suturing or wound care. Toward the end of the day, you may address documentation issues in patients’ charts.
Read more on Where Can Medical Assistants Work?
Phlebotomists: Overview
Phlebotomists are vital in ensuring accurate laboratory diagnostics, with typical duties that may involve:
- Collecting blood and other specimens from patients
- Labeling and appropriately storing blood specimens
- Preparing blood specimens for transport to the laboratory
- Maintaining equipment and inventory related to phlebotomy
- Educating patients about the process of lab work and specimen collection
To pursue a career as a phlebotomist, you typically need to meet specific qualifications, including:
- Obtaining a high school diploma or GED equivalent
- Completing a formal training program in phlebotomy or having one year of supervised work experience in phlebotomy.
Phlebotomists are employed in various settings requiring lab work, such as hospitals, urgent care clinics, diagnostic labs, blood banks, and blood donor centers.
Work hours for phlebotomists may vary, with some working regular weekday shifts, while others may need to work nights and weekends.
While the primary task of a phlebotomist is to collect blood and other specimens from patients, the day-to-day work can differ. For instance, you may need to provide exceptional care when collecting blood from infants or elderly patients.
Additionally, you may have to reassure and calm nervous patients with concerns about blood collection.
See: Can Medical Assistants Draw Blood?
Significant Differences Between a Phlebotomist and a Medical Assistant
Even though medical assistants and phlebotomists share some similarities in their job roles, there are notable differences between these two careers.
Some of the key differences between medical assistants and phlebotomists are-
- A diverse range of duties-
Medical assistants typically have a more comprehensive range of responsibilities compared to phlebotomists. In addition to blood collection, medical assistants may take patient vital signs, assist with procedures, and schedule appointments, among other duties. - Specialized training in blood collection-
Phlebotomists receive more specialized training in blood collection techniques compared to medical assistants, as it is their primary responsibility. As a result, phlebotomists are generally more experienced and skilled in this area. - Workplace settings-
Phlebotomists are more likely to work in hospitals or diagnostic laboratories with more lab specimen collection. On the other hand, medical assistants are more commonly employed in clinics or physician’s offices, where they work closely with physicians and advanced practice providers.
These differences highlight the varying scopes of practice and workplace settings for medical assistants and phlebotomists.
It’s important to understand these differences if you are considering a career in either field and to pursue the proper education and training to excel in the chosen role.
Also see: Is Medical Assistant a Good Career?
Major Similarities Between Medical Assistants and Phlebotomists
Despite the differences, medical assistants and phlebotomists also share several key similarities in their roles and responsibilities. These similarities include the following-
- Specialized training-
Both medical assistants and phlebotomists require formal training or supervised work experience to perform their jobs effectively. High school completion or GED is typically required, followed by specialized training in their respective fields. - People skills-
Both medical assistants and phlebotomists work directly with patients, so excellent interpersonal skills are essential. They need to communicate effectively, provide compassionate care, and interact with diverse personalities to ensure positive patient outcomes. - Flexibility and ability to work under stress-
The work of medical assistants and phlebotomists can be unpredictable and fast-paced, requiring them to be flexible and adaptable to changing circumstances. They also need to handle stress well, stay calm under pressure, and maintain accuracy in their work. - Understanding basic medical terminology-
Both medical assistants and phlebotomists need to have a solid understanding of basic medical assistant terminology to communicate effectively with coworkers and patients and to perform their duties accurately. - Blood drawing-
While phlebotomists specialize in blood collection, medical assistants may also be trained and certified to draw blood under the supervision of a licensed physician. Medical assistants may undergo additional phlebotomy training to gain this skill.
Phlebotomists and Medical Assistants: Job Growth & Salaries
Qualified healthcare professionals, such as medical assistants and phlebotomists, are in high demand in the United States, and both professions offer comparable salaries and job growth opportunities.
(Also Read: Medical Assistant On-the-Job Training)
The average salary for medical assistants, as reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, is $37,190. On the other hand, phlebotomists earn an average salary of $37,380.
These figures are subject to change across different locations and are dependent on various factors such as certifications, experience, and level of education.
The U. S. BLS also further reported that both fields are projected to experience substantial job growth from 2021 to 2031, with medical assistants expected to grow by 16% and phlebotomists by 10%.
See more: Medical Assistant Job Outlook
The job growth is, therefore, more than average for both professions, making them ideal careers to start with.
Read more on Certified Medical Assistant Salary
Educational and Training Requirements for Phlebotomists and Medical Assistants
While medical assistants and phlebotomists require a high school diploma or GED as an essential requirement, their training paths differ significantly despite entry-level healthcare jobs.
Phlebotomists typically need to complete a formal certificate or diploma program, which can range from as short as five weeks to several months, depending on the school.
These programs cover various topics such as human anatomy, medical terminology, and specimen collection techniques.
Many phlebotomy programs also include an externship component that allows students to gain practical experience in collecting blood specimens.
Also see: Medical Assistant Externship
Additionally, to be eligible for the certification exam, phlebotomists are typically required to provide documentation of performing a certain number of vein sticks and capillary sticks on living individuals, usually 30 vein sticks and 10 capillary sticks.
In contrast, medical assistants typically undergo a longer training program due to their broader scope of responsibilities. Medical assistant programs can range from about six months to up to two years.
Medical assistant programs cover a wide range of topics, including medical billing, coding, anatomy, and clinical procedures. They often include a clinical component where students gain hands-on experience by working in physician offices or clinics.
See: How to get Medical Assistant jobs with no experience
After completing their training program, students can take an exam to obtain their medical assistant certification.
Also read: Which Medical Certification is the Best?
Here is more on: Medical Assistant Educational Requirements
A Day in the Life of a Medical Assistant vs a Phlebotomist
Both medical assistants and phlebotomists are essential in delivering healthcare services to patients and may have some overlapping responsibilities when working in similar settings. For instance, both may collect blood specimens and educate patients on lab processes.
However, as a medical assistant, most of your day will likely be focused on providing direct patient care. This may involve taking vital signs, collecting medical history, and assisting physicians with exams and procedures.
Medical assistants may also be responsible for scheduling appointments and handling billing, coding, and insurance tasks.
On the other hand, phlebotomists primarily specialize in blood collection and related procedures. Their day-to-day work may involve drawing blood, preparing specimens for testing, and following proper lab procedures.
Also see: Medical Assistant vs Medical Billing and Coding

Do You Want To Become a Medical Assistant? Check Out Free Medical Assistant Masterclass!
In our masterclass you learn:
- How to be a medical assistant faster…in just 4 months!
- Avoid student debt & driving to classes
- #1 thing employers want from Medical Assistants
- How to stand-apart & get a university certificate for a strong resume
Conclusion
Indeed, while medical assistants may have a more diverse range of responsibilities, their training programs can be longer than phlebotomists.
Phlebotomist students may enter the job market relatively quickly due to the concise coursework, but their scope of practice may be more limited than medical assistants.
Despite these differences, medical assistants and phlebotomists play meaningful roles in healthcare. Both professions offer good job growth prospects and decent pay for the training time invested.
Either option can serve as an excellent first step towards a fulfilling and rewarding career in healthcare.
Also see: Medical Assistant Career Path
Related Resources:
- How To Become a Medical Assistant
- How Long Does It Take To Become a Medical Assistant
- Medical Assistant Skills
- Certified Clinical Medical Assistant
- Medical Administrative Assistant
- CMA vs CNA
- CMAA vs CCMA
- Military Medical Assistant
- Medical Assistant vs EMT
- Accelerated Medical Assistant Program
- National Certified Medical Assistant NCMA
- Medical Assistant Degree Online 6 Weeks
- Medical Assistant Courses
- 4 Week Medical Assistant Program
Related Articles
-
How to Be Successful in College in 2022 – 7 Simple Tips to Succeed
-
How Do Scholarships Work? Read This First…Truth is Shocking
-
7 Best College Majors 2024: What Should I Major In?
-
How to Choose a College – 10 Things You Must Consider in 2024
-
Why Go to College? Top 13 Benefits for Adult Students in 2022
-
Top 5 Best Alternatives to Community College for 2024