If you have been wanting to get into the healthcare industry and on the frontlines, you might be considering becoming either an emergency medical technician (EMT) or a medical assistant.
Medical assistants are healthcare workers that provide support services to physicians and other healthcare professionals.
Medical assistant job duties include administrative and clinical duties, ranging from assisting physicians with bedside procedures to scheduling appointments.
What is an EMT?
An emergency medical technician (EMT) is a healthcare worker that usually works in an ambulance and responds to emergency medical calls, performs primary emergency medicine, and transports patients to the hospital.
Read on to learn more about the similarities and differences between the two professions and educational requirements to help you decide which career might be the best fit for you.
Also see: Is Medical Assistant a Good Career?
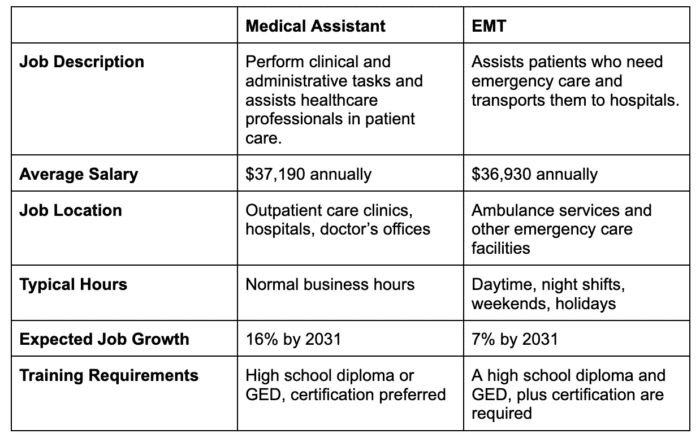
Medical Assistant vs EMT: An Overview
While both medical professions share similarities, there are also significant differences between the two.
Both roles involve providing direct care to patients and require some level of medical knowledge. However, the main difference lies in the work environment.
Medical assistants offer care in a controlled, non-emergency setting, whereas EMTs provide care in an unpredictable and often emergency environment.
See: 12 Reasons to Become a Medical Assistant
Additionally, medical assistants tend to have more administrative responsibilities compared to EMTs.
Here is a brief overview of each profession:
Medical Assistant: Overview
Medical assistants perform a variety of tasks in both the front office and clinical care areas of a doctor’s office or clinic.
Their responsibilities generally include:
1. Scheduling appointments: Medical assistants handle the coordination of patient appointments, ensuring a smooth and organized schedule.
2. Answering phones: They manage incoming calls, addressing inquiries and providing necessary information to patients or directing calls to the appropriate staff members.
3. Giving injections: Medical assistants are trained to administer injections, such as vaccines or medications, under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
4. Taking vital signs: They measure and record vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, and respiratory rate, to assist in patient assessments.
5. Drawing blood: Medical assistants proficient in phlebotomy collect blood samples from patients for laboratory testing, ensuring proper handling and labeling.
Also see: Can Medical Assistants Draw Blood?
6. Cleaning patient rooms: They maintain cleanliness and hygiene in patient examination rooms, preparing them for each patient and ensuring a safe and sanitary environment.
7. Stocking supplies: Medical assistants monitor and restock medical supplies and equipment, ensuring they are readily available for patient care and procedures.
It’s important to note that the specific responsibilities of medical assistants can vary depending on the type of healthcare setting and the scope of practice allowed in their state or organization.
See also: Medical Assistant scope of practice by state
To become a medical assistant, a high school diploma or GED is usually required.
Many employers prefer candidates who have completed a medical assistant program and passed a certification exam, although it is possible to get a medical assistant job without prior experience or certification.
Medical assistants typically work regular business hours, aligning with the operating hours of doctors’ offices. They typically do not have to work on holidays or weekends and can expect to be home for dinner.
Read more on: How to become a Medical Assistant
EMT: Overview
EMTs (Emergency Medical Technicians) primarily work in ambulatory health settings and can be found at events with large crowds. They are typically part of an ambulance or medical transport team.
The responsibilities of an EMT include:
1. Measuring vital signs: EMTs assess and monitor vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and oxygen levels to evaluate a patient’s condition.
2. Driving emergency vehicles: EMTs are trained to operate and drive emergency vehicles, such as ambulances, safely and efficiently to transport patients to medical facilities.
3. Providing emergency first aid: EMTs deliver immediate medical care and first aid to patients in emergency situations, addressing injuries, controlling bleeding, immobilizing fractures, and managing other urgent medical needs.
4. Performing CPR: EMTs are skilled in performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to revive individuals experiencing cardiac arrest or respiratory failure.
5. Administering some medications: EMTs may have authorization to administer certain medications, such as epinephrine for severe allergic reactions or naloxone for opioid overdose emergencies.
6. Assisting with bag-valve-mask ventilation: EMTs are trained to provide assistance to patients who have difficulty breathing by using a bag-valve-mask device to deliver oxygen.
To become an EMT, individuals must have a high school diploma or GED before enrolling in an EMT training program. Completion of the program and obtaining a certificate are necessary to start working as an EMT.
See: Accelerated Medical Assistant Program
EMTs are often required to work non-traditional hours, including nights, weekends, and holidays.
This is because emergencies can occur at any time, and the round-the-clock availability of emergency medical services is essential to provide timely assistance to those in need.
Also read: Medical Assistant Certificate Requirements
Major Similarities Between EMTs and Medical Assistants
Medical assistants and EMTs, although distinct roles, share certain similarities:
- Patient care: Both medical assistants and EMTs are involved in providing care to patients. They measure vital signs and offer basic assistance to individuals in need.
- Comparable salaries: The average salaries for medical assistants and EMTs are relatively similar, with only a small difference of a few hundred dollars per year. Medical assistants earn an average of $37,190 annually, while EMTs earn around $36,930.
- Education requirements: Both positions are considered entry-level healthcare roles with minimal educational prerequisites. While certification is not mandatory for medical assistants, it is highly recommended. Certification requirements for medical assistants and EMTs are somewhat similar.
- Exposure to bodily fluids: Both medical assistants and EMTs encounter bodily fluids as part of their duties. They may regularly come into contact with blood, urine, and stool.
Also see: Medical Assistant Educational Requirements
Major Differences Between EMTs and Medical Assistants
Medical assistants and EMTs differ significantly in various aspects of their job responsibilities and work environments:
- Workflow predictability: Medical assistants typically have a structured and predictable workflow. They follow a schedule, spend a set amount of time with each patient (usually 15 to 30 minutes), and have a general idea of the types of care they will provide throughout the day. In contrast, EMTs experience an unpredictable workflow. They can encounter a variable number of patients, ranging from multiple cases in a day to just one, and respond to diverse emergencies, making their day-to-day work highly unpredictable.
- Job growth outlook: While both professions have positive job growth outlooks, medical assistants are projected to have a higher increase in job opportunities compared to EMTs. The demand for medical assistants is expected to grow at a faster rate, offering more employment prospects.
- Work environment: Medical assistants predominantly work in clinical settings such as clinics, medical offices, and occasionally hospitals. They generally operate within a controlled indoor environment.EMTs, on the other hand, typically work for ambulance services or ambulatory care settings. They often travel to various locations and may provide care in diverse settings such as outdoor environments, people’s homes, or large sporting events.
Also read: Certified Clinical Medical Assistant
Medical Assistant vs EMT: Job Growth & Salary Comparison
Medical assistants and EMTs generally receive similar salaries and are considered entry-level positions within the healthcare industry.
The average annual salary for a medical assistant is approximately $37,190, equivalent to an hourly rate of $17.88. Similarly, EMTs earn an average annual salary of around $36,930, with an hourly rate of $17.76.
It’s important to note that these salary figures can vary depending on factors such as the specific city or location of employment, years of experience, and additional certifications held by the individuals.
Also read: Certified Medical Assistant Salary
Both medical assistants and EMTs have positive job outlooks. The employment opportunities for medical assistants are projected to grow by 16% through 2031, significantly faster than the national average for all occupations.
EMTs can also anticipate a 7% growth in job opportunities through 2031, which is still higher than the overall average.
See more on: Medical Assistant Job Outlook
Medical Assistant vs. EMT: Salary by State
| State | EMT Annual Salary | Medical Assistant Annual Salary |
| Alabama | $28,030 | $31,390 |
| Alaska | $51,330 | $46,390 |
| Arizona | $33,840 | $37,790 |
| Arkansas | $30,580 | $32,170 |
| California | $42,420 | $44,780 |
| Colorado | $35,590 | $40,270 |
| Connecticut | $41,120 | $41,010 |
| Delaware | $39,090 | $36,450 |
| District of Columbia | $48,500 | $46,690 |
| Florida | $33,090 | $35,480 |
| Georgia | $32,470 | $35,470 |
| Hawaii | $55,600 | $42,460 |
| Idaho | $33,080 | $37,650 |
| Illinois | $44,460 | $37,910 |
| Indiana | $32,470 | $36,600 |
| Iowa | $32,570 | $38,290 |
| Kansas | $26,190 | $34,270 |
| Kentucky | $29,250 | $33,360 |
| Louisiana | $35,020 | $30,620 |
| Maine | $32,710 | $38,990 |
| Maryland | $50,770 | $39,280 |
| Massachusetts | $43,160 | $44,200 |
| Michigan | $31,650 | $35,640 |
| Minnesota | $38,200 | $44,010 |
| Mississippi | $29,350 | $31,640 |
| Missouri | $33,560 | $34,380 |
| Montana | $31,940 | $39,000 |
| Nebraska | $33,970 | $36,560 |
| Nevada | $33,490 | $36,890 |
| New Hampshire | $35,670 | $40,370 |
| New Jersey | $40,360 | $39,600 |
| New Mexico | $34,620 | $34,470 |
| New York | $41,120 | $42,100 |
| North Carolina | $36,090 | $35,650 |
| North Dakota | $34,150 | $37,440 |
| Ohio | $32,760 | $35,330 |
| Oklahoma | $27,980 | $32,230 |
| Oregon | $37,040/td> | $44,000 |
| Pennsylvania | $33,450 | $36,750 |
| Rhode Island | $42,460 | $39,390 |
| South Carolina | $35,140 | $34,270 |
| South Dakota | $32,570 | $33,880 |
| Tennessee | $35,400 | $35,150 |
| Texas | $34,070 | $34,600 |
| Utah | $32,350 | $35,570 |
| Vermont | $36,070 | $39,220 |
| Virginia | $36,770 | $38,330 |
| Washington | $37,500 | $47,320 |
| West Virginia | $28,530 | $31,230 |
| Wisconsin | $32,440 | $39,670 |
| Wyoming | $32,410 | $37,470 |
| Guam | $33,870 | $26,060 |
| Puerto Rico | $28,040 | $23,450 |
Medical Assistants vs EMTs: Educational & Certification Requirements
Both medical assistants and EMTs need medical knowledge and skills for their jobs. They must think critically and work well with others.
Medical assistants can start working right after high school or getting a GED. However, many employers prefer certified medical assistants.
You can complete certification courses for medical assistants at colleges, technical schools, or online programs.
These programs typically take 4 months to 2 years. After finishing the course, you need to pass an exam to earn your certificate.
Also see: How Long Does it Take to Become a Medical Assistant?
Before starting work as an EMT, you must complete an EMT certification course. Having a high school diploma or GED is necessary for enrolling in the course.
The course covers important topics like airways, cardiology and resuscitation, EMS transport, emergency medical care, and obstetrics.
Accelerated programs such as online courses can be completed in as little as 4 months, while degree programs can take up to 2 years. Additionally, EMTs need to pass a physical test to ensure they are physically capable of performing their duties.
See also: Medical Assistant Skills
More on: Medical Assistant Programs Cost

Do You Want To Become a Medical Assistant? Check Out Free Medical Assistant Masterclass!
In our masterclass you learn:
- How to be a medical assistant faster…in just 4 months!
- Avoid student debt & driving to classes
- #1 thing employers want from Medical Assistants
- How to stand-apart & get a university certificate for a strong resume
A Day in the Life of a Medical Assistant vs an EMT
A day in the life of a medical assistant and an EMT can vary significantly.
Medical assistants typically start their day by preparing the clinic or office for operation. This involves tasks like setting up patient rooms, ensuring adequate supplies are available, and sending out appointment reminders.
Throughout the day, they assist patients with routine appointments, take vital signs, and provide support during bedside procedures. They may also spend a significant amount of time working on the computer and answering phone calls.
On the other hand, EMTs have a more dynamic work environment. They are often dispatched to emergency scenes or respond to urgent medical calls.
EMTs provide immediate medical assistance at the location, assess patients’ conditions, administer necessary treatments, and transport patients to medical facilities if required.
Their work involves quick decision-making and teamwork in high-pressure situations.
While medical assistants focus on providing comprehensive support in a clinical setting, EMTs play a crucial role in emergency medical response and pre-hospital care.
Also see: How to get Medical Assistant jobs with no experience
Related Resources:
- CMA vs CNA
- CMAA vs CCMA
- Are Medical Assistant Licenses Required?
- Medical Assistant Interview Questions
- Is Medical Assistant Degree Required?
- Medical Assistant On-the-Job Training
- National Certified Medical Assistant NCMA
- Medical Assistant Courses
- Cheapest Medical Assistant Program
- 4 Week Medical Assistant Program
Related Articles
-
How to Be Successful in College in 2022 – 7 Simple Tips to Succeed
-
How Do Scholarships Work? Read This First…Truth is Shocking
-
7 Best College Majors 2024: What Should I Major In?
-
How to Choose a College – 10 Things You Must Consider in 2024
-
Why Go to College? Top 13 Benefits for Adult Students in 2022
-
Top 5 Best Alternatives to Community College for 2024