Are you passionate about healthcare and want to enter the industry without spending thousands of years on schooling?
If yes, pursuing a career in sterile processing or surgical technology might be a good choice for you.
Now, you might be confused about these two careers to go for.
Let us help you with that.
In this article, we will discuss the differences between sterile processing technicians and surgical technologists, who they are, what they do, how their salaries differ, and more.
So, read on!
What is a Sterile Processing Technician?
First, let’s know what exactly is a sterile processing technician.
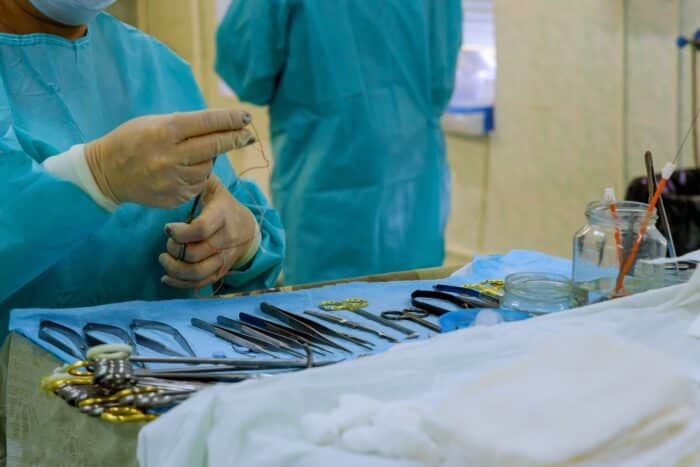
A sterile processing technician is a healthcare professional responsible for ensuring that medical equipment and instruments are properly cleaned, sterilized, and maintained to prevent infections and ensure patient safety.
They work behind the scenes in hospitals, clinics, or surgical centers, operating sterilization equipment, inspecting instruments for damage, assembling instrument trays, and following strict protocols to ensure everything is sanitized and ready for use in medical procedures.
See more: What is a Sterile Processing Technician
Sterile Processing Technician Duties
Sterile processing technicians have a range of essential duties within different healthcare settings.
Let’s take a look at them in detail:
1. Cleaning and Decontamination: They thoroughly clean, decontaminate, and sanitize medical instruments and equipment using specialized tools, detergents, and sterilization methods.
2. Sterilization Procedures: They operate sterilization equipment such as autoclaves, ensuring proper settings and procedures to effectively sterilize instruments and equipment before their use in medical procedures.
3. Inventory Management: Technicians manage inventory levels, ensuring an adequate supply of sterile instruments and equipment while maintaining accurate records of items processed.
4. Quality Control: They inspect instruments for damage, functionality, and cleanliness, ensuring they meet quality standards and following protocols for maintenance and repair when needed.
5. Assembling and Packaging: Technicians assemble and organize instrument trays and packs, ensuring they are properly wrapped and packaged for sterilization.
6. Adherence to Regulations: They adhere strictly to safety and infection control regulations, following established protocols to maintain a sterile environment and prevent healthcare-associated infections.
7. Collaboration: Technicians often collaborate with nurses, surgeons, and other healthcare professionals to ensure the availability of sterile instruments for medical procedures.
How to Become a Sterile Processing Technician
Becoming a sterile processing technician involves a few simple steps.
First, completing a high school diploma or a GED is necessary. After this, enrolling in a sterile processing training program and sitting for certification exams is important since most employers look for candidates who have completed some form of training.
Training programs for sterile processing technicians are available online and on campus. Opting for an online program is often recommended due to its advantages, such as quicker course completion, cost-effectiveness, and the flexibility to learn at your preferred pace and schedule.
Choosing an accredited training program is also recommended as it helps in preparation for certification exams. Commonly recognized certifications for sterile processing technicians include the CRCST certification provided by IAHCSMM and the CSPDT certification offered by CBSPD.
Sterile processing technicians typically work in hospitals, outpatient care centers, surgical centers, and various healthcare facilities, playing a fundamental role in maintaining sterile equipment necessary for medical procedures.
Their work schedule commonly involves weekdays during regular business hours, typically from 8 AM to 6 PM. However, some may need to work evening or night shifts depending on the healthcare setting’s requirements.
Read: Best Online Sterile Processing Course
Learn more about Preppy’s Online Sterile Processing Tech Training Program here>
What is a Surgical Technologist?
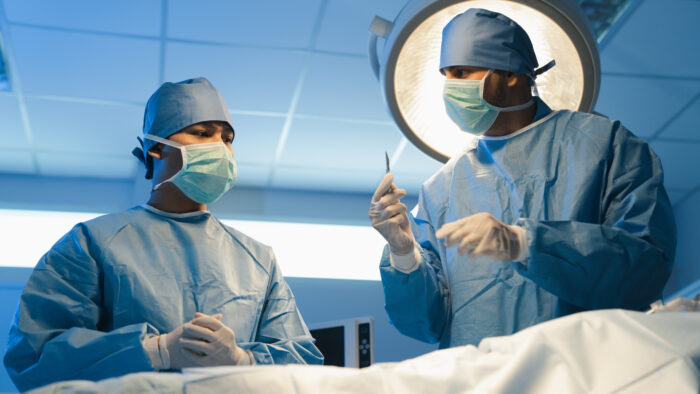
A surgical technologist, also called a scrub tech or operating room tech, is an important surgical team member. They assist surgeons, nurses, and other medical staff before, during, and after surgical procedures.
They might assist with patient preparation and help maintain accurate records of procedures. Their role is integral to the smooth functioning of surgeries, ensuring safety and efficiency within the operating room.
Surgical Technologist Duties
Surgical technologists play an essential role in the operating room before, during, and after surgeries.
Their duties typically include:
1. Preparing the Operating Room: They set up surgical instruments, equipment, and supplies required for specific procedures, ensuring everything is sterile and ready for use.
2. Assisting Surgeons and Nurses: During surgery, they pass instruments and supplies to the surgeon and assistant as needed, anticipating their requirements to maintain a smooth flow.
3. Maintaining Sterile Conditions: They enforce and monitor sterile techniques throughout the surgical procedure to minimize the risk of infections or complications.
4. Preparing Patients: They help position and prepare patients for surgery, ensuring they’re in the correct position and assisting with draping and prepping the surgical site.
5. Handling Surgical Instruments: Sterilizing, organizing, and handing instruments to surgeons and assistants during procedures, as well as ensuring proper disposal or cleaning afterward.
6. Managing Equipment: They may operate and maintain surgical equipment, including lights, suction machines, and sterilizers, ensuring everything functions properly.
7. Documentation: Keeping accurate records of surgical procedures, including counts of sponges, needles, and instruments used during surgery.
Read More on: What Does a Sterile Processing Technician Do?
How to Become a Surgical Technologist
Similar to sterile processing techs, becoming a surgical technologist involves starting with completing a high school diploma or equivalent.
Next, enrollment in a surgical technologist training program and passing certification exams are necessary. These programs are available both online and on-campus, with online options offering advantages like quicker completion, cost-effectiveness, and the flexibility to learn at one’s preferred pace and schedule.
Opting for an accredited training program is always a better idea as it helps in better preparation for certification exams. The CCST certification, offered by the NBSTSA, is widely accepted.
Surgical techs often work in operating rooms during scheduled surgeries. Their schedules can differ significantly, and they might work different shifts, including day shifts, evening shifts, or even overnight shifts in hospitals that have 24/7 surgical services.
More on: How to Become a Sterile Processing Technician
Similarities Between Sterile Processing Technicians & Surgical Technologists
Even though both careers are essential in healthcare, there are some key differences between them.
However, there are also major similarities. Let’s take a look at some of them:
1. Sterile Environment Maintenance: Both SPTs and surgical technologists play important roles in maintaining a sterile environment in the operating room. SPTs ensure that surgical instruments and equipment are properly sterilized, while surgical technologists assist in creating and maintaining a sterile field during surgical procedures.
2. Instrument Handling: Both professionals are involved in handling surgical instruments. SPTs clean, disinfect, and sterilize instruments, ensuring they are ready for use. Surgical technologists assist surgeons by passing instruments during procedures and ensuring they have the necessary tools readily available.
3. Patient Safety: Both roles are centered around ensuring patient safety. SPTs ensure that instruments are properly cleaned and sterilized to prevent infections, while surgical technologists contribute to maintaining a sterile environment during surgeries to minimize the risk of complications for patients.
4. Collaborative Teamwork: Both SPTs and surgical technologists are integral members of the surgical team. They collaborate closely with surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to ensure that surgeries proceed smoothly and safely.
5. Knowledge of Surgical Procedures: While SPTs may not be directly involved in surgeries, they often have a basic understanding of surgical procedures and instruments. Surgical technologists, on the other hand, have in-depth knowledge of surgical procedures, assisting surgeons during operations and anticipating their needs.
See more: Sterile Processing Technician Certification
Differences Between Sterile Processing Technicians & Surgical Technologists
As mentioned earlier, sterile processing technicians (SPTs) and surgical technologists have varied roles within the healthcare system, each with specific responsibilities.
Let’s see how they differ:
Primary Focus:
SPTs primarily focus on cleaning, disinfecting, sterilizing, and organizing surgical instruments and equipment. They work behind the scenes to ensure instruments are properly processed and ready for surgical use.
Surgical technologists are directly involved in surgical procedures. They assist surgeons during operations, prepare the operating room, and handle instruments and supplies during surgeries, actively participating in patient care.
Direct Patient Interaction:
While SPTs contribute significantly to patient safety by ensuring sterile instruments, they usually do not have direct patient interaction during surgeries.
Surgical techs, on the other hand, work closely with patients in the operating room, assisting in positioning them, preparing surgical sites, and addressing immediate surgical needs under the supervision of surgeons.
Level of Education and Training:
Typically, SPTs undergo training programs or certification courses that focus on sterile processing techniques, infection control, and proper handling of instruments and equipment.
Surgical technologists undergo more extensive education and training programs that include a wider range of surgical procedures, anatomy, and patient care within the operating room environment.
Responsibility During Surgeries:
SPTs are responsible for ensuring that sterilized instruments and equipment are readily available for surgical procedures but do not participate directly in surgeries.
Surgical techs play an active role in surgeries by passing instruments, maintaining a sterile field, and assisting surgeons, contributing to the successful execution of surgical procedures.
Work Setting:
SPTs primarily work in central sterile processing departments or sterile processing units within healthcare facilities.
Surgical Techs work directly in operating rooms, surgical centers, hospitals, or other healthcare settings where surgeries take place.
See: Certified Sterile Processing Technician
Educational Requirements for Sterile Processing Techs vs Surgical Technologists
The educational requirements for sterile processing technicians (SPTs) and surgical technologists are different. SPTs usually enter the field with a high school diploma and might receive on-the-job training or opt for certificate programs emphasizing sterilization techniques and safety protocols. Pursuing certifications like the CRCST or CSPDT can enhance their job prospects, even though they are not mandatory.
On the other hand, surgical technologists undergo more comprehensive education, typically completing accredited programs covering anatomy, surgical procedures, and patient care in the operating room. Employers often seek candidates with diplomas, certificates, or associate degrees from recognized surgical technology programs.
Certification, particularly the CST credential provided by the NBSTSA, is commonly preferred or required, which requires program completion and a successful certification exam to qualify.
What a Day in the Life of a Sterile Processing Technician vs. a Surgical Technologist Looks Like
A day in the life of a sterile processing technician (SPT) typically starts in the central processing department of a healthcare facility.
Their routine involves receiving, cleaning, disinfecting, and sterilizing surgical instruments and equipment. They have to assemble and package sterilized items, maintaining precise organization for quick access by surgical teams.
Continuous quality checks and equipment monitoring ensure adherence to stringent cleanliness and safety standards. Additionally, SPTs manage inventory, ensuring an ample supply of sterilized instruments while promptly ordering necessary supplies.
On the other hand, the daily responsibilities of a surgical technologist revolve around the setting of the operating room. They prepare the space, arranging surgical tools and supplies while maintaining a sterile environment.
During surgeries, their role involves close collaboration with surgeons, passing instruments, and proactively meeting their needs. Surgical technologists also engage in patient care, assisting in patient positioning, ensuring comfort, and preparing surgical sites.
Accurate documentation of procedures, including instrument counts, is also an important part of their responsibilities, which tells us about their integral role in surgical procedures and patient care within the operating room.
Also See: Travel Sterile Processing Technician
Conclusion
In the world of healthcare, the roles of sterile processing technicians and surgical technologists are both important yet different.
Sterile processing technicians ensure the safety and sterility of instruments behind the scenes, while surgical technologists actively participate in surgeries, supporting both surgeons and patients in the operating room.
Both professions play integral parts in surgical care, each contributing in its unique way to the success and safety of medical procedures.
Related Resources:
- Sterile Processing Technician Salary
- Sterile Processing Technician Job Description
- Sterile Processing Technician Requirements
- Sterile Processing Technician Resume
- Sterile Processing Technician School
- Sterile Processing Technician Course
- Sterile Processing Technician Training Program Cost
- CRCST Certification
Related Articles
-
How to Be Successful in College in 2022 – 7 Simple Tips to Succeed
-
How Do Scholarships Work? Read This First…Truth is Shocking
-
7 Best College Majors 2024: What Should I Major In?
-
How to Choose a College – 10 Things You Must Consider in 2024
-
Why Go to College? Top 13 Benefits for Adult Students in 2022
-
Top 5 Best Alternatives to Community College for 2024